Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Methods
Connectors
Most vehicles have two charging sockets, one for AC charging at home or the workplace, and one for DC charging at high speed charging stations. Each of these charging sockets can vary depending on the market the vehicle was manufactured for.
AC - Slow to medium speed
AC charging stations deliver mains AC current to the vehicle, requiring the vehicle’s on-board charger to rectify the AC current to DC and manage the charging process.
Type 1
Type 2
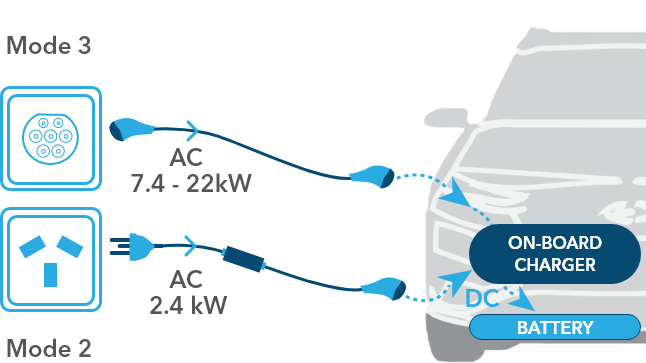
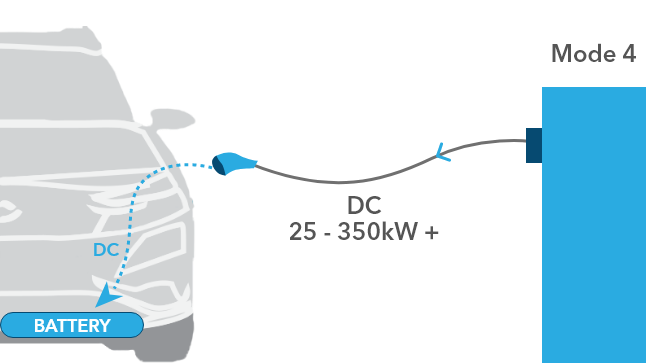
DC - Fast to rapid speed
DC charging stations deliver high voltage DC current directly to the vehicle battery, bypassing the vehicle’s on-board charger.

CHAdeMO
CCS
Typical charging times
There are two main factors that determine how fast the electric vehicle will charge, firstly the speed of the charging station, but also the maximum supported charging speed of the EV itself. For example, a 2014 Nissan Leaf only supports a maximum charging speed of 3.7kW, even if plugged into a 7.4kW charging station.
| Type of Charger | Speed | Range added per hour | Charging Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 amp portable charger | 1.5kW | 10km | 35 hours |
| AC single-phase | 7.4kW | 40km | 9 hours |
| AC three-phase | 22kW | 120km | 3 hours |
| DC medium | 25kW | 150km | 1.5 hours (to 80%) |
| DC rapid | 50kW | 300km | 1 hour (to 80%) |
| DC ultra-rapid | 175kW | 300km | 15 min (to 80%) |
* The information in the above table is approximate and charging times are based on a vehicle with a 64kWh battery. Note that only some EVs will accept higher delivery speeds from ultra rapid chargers.
Get a Free Consultation
Call us today or simply click the button

